Vein ablation is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat varicose veins and underlying venous insufficiency by closing off or destroying diseased veins. It is commonly performed to alleviate symptoms such as pain, swelling, and discomfort associated with varicose veins and to improve venous circulation in the legs.
Causes
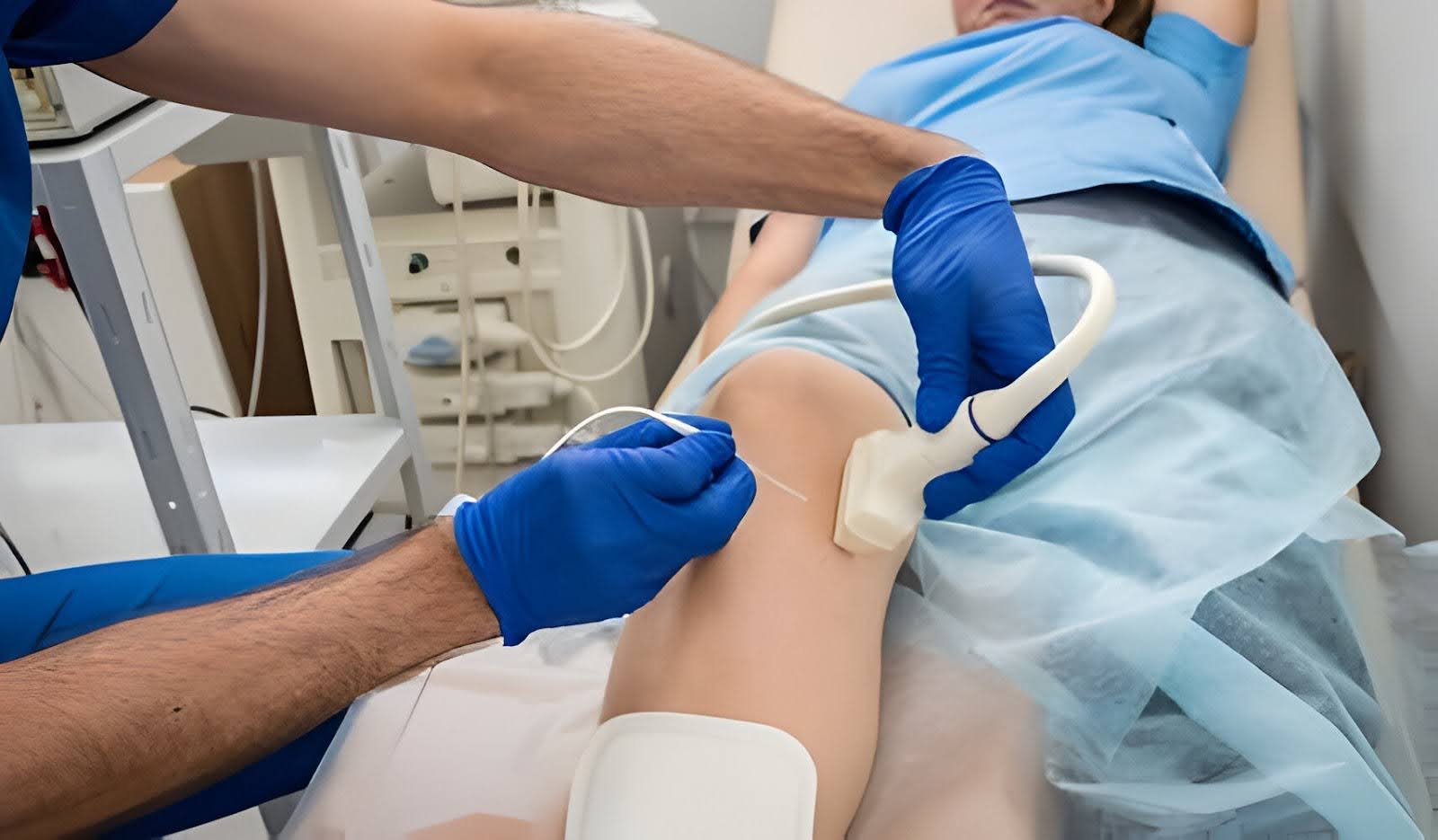
The vein ablation procedure typically involves the following steps:- Preparation: The patient lies comfortably on an examination table, and the treatment area is cleansed and sterilized. Local anesthesia is administered to numb the skin and surrounding tissues.
- Vein Mapping: Using ultrasound guidance, the healthcare provider identifies the diseased veins and maps out their course to guide the placement of the ablation catheter.
- Insertion of Ablation Catheter: A thin, flexible catheter is inserted into the diseased vein through a small incision or needle puncture in the skin. The catheter is advanced into the vein under ultrasound guidance until it reaches the desired treatment site.
-
Ablation Procedure: Once the catheter is in position, the ablation technique is performed to close off the diseased vein. There are two main types of vein ablation procedures:
- Endovenous Laser Ablation (EVLA): Laser energy is delivered through the catheter to heat and seal the vein from the inside, causing it to collapse and eventually be reabsorbed by the body.
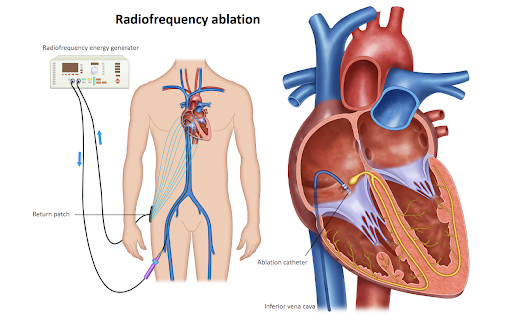
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): Radiofrequency energy is delivered through the catheter to heat and shrink the vein wall, leading to closure of the vein.
- Confirmation of Closure: After the ablation procedure is completed, ultrasound imaging may be used to confirm closure of the treated vein and assess for any residual flow or complications.
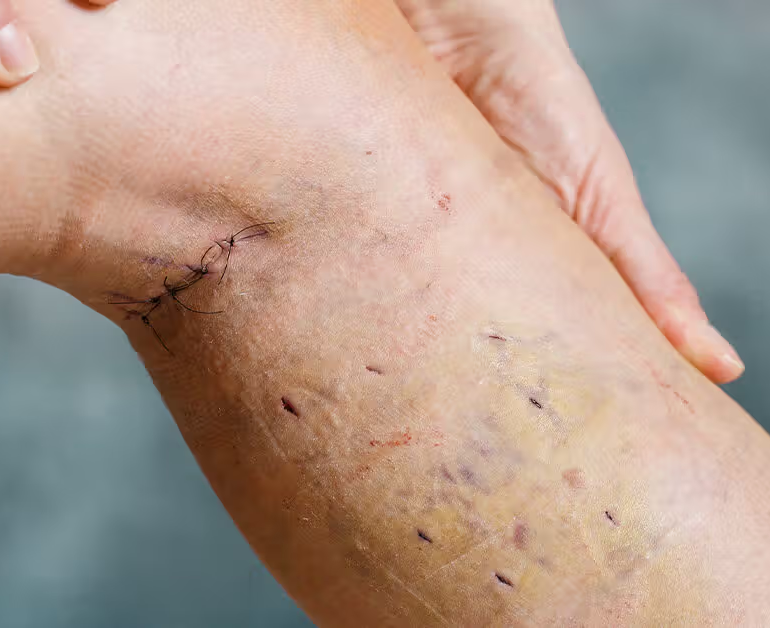
- Bandaging and Compression: The treatment site is typically bandaged, and compression stockings or bandages may be applied to promote healing and reduce swelling.
Indications
Vein ablation may be indicated for patients with symptomatic varicose veins and underlying venous insufficiency, especially those experiencing symptoms such as:- Pain or discomfort in the legs
- Swelling (edema) or heaviness in the legs
- Skin changes or discoloration
- Ulcers or sores on the legs
- Visible varicose veins or spider veins
Benefits
Vein ablation offers several benefits for patients with varicose veins and venous insufficiency, including:- Minimally invasive: The procedure is performed using a small incision or needle puncture, resulting in less trauma and faster recovery compared to traditional vein stripping surgery.
- Effective: Vein ablation provides long-term closure of diseased veins, leading to symptom relief and improvement in venous circulation.
- Outpatient procedure: Vein ablation can typically be performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home the same day and resume normal activities within a few days.
- High success rate: Vein ablation has a high success rate in closing off diseased veins and improving symptoms, with low rates of recurrence and complications.
Complications
Although vein ablation is considered safe and effective, potential complications may include:- Bruising or discomfort at the treatment site
- Infection or inflammation
- Nerve injury or numbness
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Skin burns or discoloration
- Allergic reaction to anesthesia or contrast agents