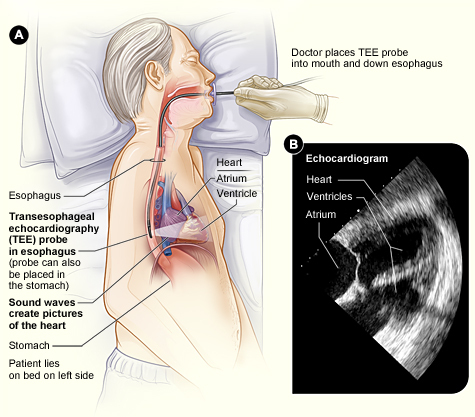
A transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) is a specialized type of echocardiogram that provides detailed images of the heart’s structure and function by using a probe inserted into the esophagus (the swallowing tube) instead of being placed on the chest wall externally. TEE offers several advantages over a standard transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE), particularly when higher-resolution images are needed or when TTE is inconclusive.
Procedure
During a TEE, the patient is typically given a sedative to help them relax and prevent discomfort. A thin, flexible probe with an ultrasound transducer at its tip is then passed through the mouth and down the throat into the esophagus, which lies directly behind the heart. Because the esophagus is close to the heart, TEE provides closer and clearer images of the heart’s structures compared to TTE.Uses of TEE
Transesophageal echocardiography is used for various diagnostic and interventional purposes, including:- Assessment of Valve Function: TEE provides detailed images of heart valves and helps evaluate the severity of valve disorders, such as stenosis, regurgitation, or prosthetic valve dysfunction.
- Detection of Cardiac Masses and Clots: TEE can detect abnormal growths or masses within the heart, such as tumors, vegetations (infective endocarditis), or blood clots (thrombi).
- Evaluation of Aortic Diseases: TEE assesses the aorta and aortic valve for conditions such as aortic dissection, aneurysm, or atherosclerosis.
- Monitoring during Cardiac Surgery: TEE is often used during cardiac surgeries to monitor the heart’s function in real time and guide surgical interventions, such as valve repair or closure of septal defects
- Assessment of Congenital Heart Disease: TEE provides detailed images of the heart’s structures and helps diagnose and evaluate congenital heart defects, such as atrial septal defects or patent foramen ovale.
Advantages of TEE
Transesophageal echocardiography offers several advantages over transthoracic echocardiography, including:- Higher Resolution: TEE provides closer and clearer images of the heart’s structures compared to TTE, allowing for better visualization of certain anatomical details.
- Unobstructed View: TEE is not limited by factors such as body habitus, lung disease, or chest wall abnormalities that can affect the quality of TTE images.
- Less Interference: TEE is less affected by lung tissue and air-filled structures, resulting in clearer images of the heart.
Risks and Considerations
While TEE is generally safe, it carries some risks, including:- Discomfort or Sore Throat: Patients may experience discomfort or a sore throat after the procedure due to the presence of the probe in the esophagus.
- Complications: Rare complications of TEE may include esophageal injury, bleeding, or adverse reactions to sedation.