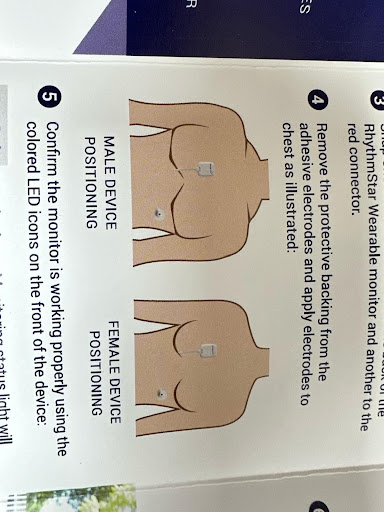
Telemetry is a method of remotely monitoring physiological parameters, such as heart rate, rhythm using wireless technology. This help to identify possible causes of patient condition including syncope.
Procedure
Telemetry involves placing sensors or electrodes on the patient’s body to measure and transmit physiological data to a central monitoring system. The sensors are connected to a bedside monitor or transmitter, which wirelessly sends the data to a central monitoring station where healthcare providers can observe the patient’s vital signs heart rate and rhythm in real time. Telemetry systems can also be programmed to trigger alarms or alerts if certain parameters exceed predefined thresholds, indicating potential medical emergencies or changes in the patient’s condition.- Continuous Monitoring: Telemetry allows for continuous monitoring of patients’ vital signs, providing healthcare providers with real-time information about changes in the patient’s condition.
- Early Detection of Deterioration: Telemetry monitoring helps identify early signs of clinical deterioration or changes in the patient’s condition that may require intervention, such as arrhythmias, hypoxemia, or changes in blood pressure.
- Postoperative Monitoring: Telemetry is often used to monitor patients after surgery, particularly in the immediate postoperative period, to detect complications such as bleeding, arrhythmias, or respiratory distress.
- Cardiac Monitoring: Telemetry units are commonly used for cardiac monitoring, particularly for patients with known or suspected heart disease, arrhythmias, or recent cardiac events such as heart attack or heart surgery.
Uses of Telemetry
Telemetry monitoring is used for various purposes in healthcare settings, including:- Critical Care Monitoring: Telemetry is frequently used in critical care units, including intensive care units (ICUs) and step-down units, to monitor patients with critical illnesses or injuries who require close observation and rapid intervention.
- Mobility: Telemetry allows patients to move around within the hospital or telemetry unit while still being monitored, promoting mobility and early ambulation.
- Remote Monitoring: Telemetry allows healthcare providers to monitor multiple patients simultaneously from a central monitoring station, improving efficiency and enabling timely intervention when needed.
- Continuous Surveillance: Telemetry provides continuous surveillance of patients’ vital signs, reducing the need for frequent manual checks and enabling early detection of changes in the patient’s condition.
Risks and Considerations
Telemetry monitoring is generally safe, but it carries some risks, including:- Bleeding: Bleeding or hematoma at the insertion site is a common complication of telemetry.
- Vascular Injury: Rarely, telemetry can cause injury to blood vessels, leading to bleeding, hematoma, or pseudoaneurysm formation.
- Allergic Reaction: Some patients may experience allergic reactions to the sensors or electrodes used during telemetry monitoring, which can range from mild to severe.
- Interference: Wireless telemetry systems may experience interference from other electronic devices, which can affect the accuracy of the monitored data.