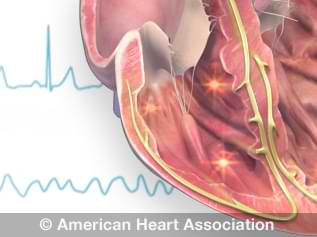
Premature heartbeats are extra beats that disrupt the regular rhythm of the heart. They are a common type of arrhythmia and are generally not harmful, though they can feel alarming. These extra beats are known as premature atrial contractions (PACs) when they originate in the atria (the heart’s upper chambers), and premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) when they occur in the ventricles (the heart’s lower chambers).
Causes
Premature heartbeats can occur in healthy people and those with heart disease. Their occurrence can be increased by:- Stress or anxiety
- Caffeine, nicotine, or alcohol use
- Certain medications, such as decongestants and antihistamines
- Hormonal changes, such as those during pregnancy
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Increased levels of adrenaline, which can be due to physical activity, anxiety, or some health conditions
Symptoms
Most premature heartbeats are asymptomatic, but when symptoms do occur, they may include:- Feeling an extra or missed beat
- Fluttering in the chest
- Pounding or jumping sensation in the chest
- Increased awareness of the heartbeats
Diagnosis:
If premature heartbeats are frequent or cause concern, the following tests might be used to evaluate them:- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) : Records the electrical signals in the heart and can detect premature beats.
- Holter monitor : A portable device worn for 24 to 48 hours to record continuous ECG data, capturing premature beats that occur during normal activity.
- Event monitor : Similar to a Holter monitor but worn for a longer period, and the patient can activate it when they feel abnormal heartbeats.
- Echocardiogram : An ultrasound of the heart that checks for structural heart problems.
Treatment:
In many cases, no treatment is necessary for premature heartbeats. However, if they are bothersome or related to an underlying heart condition, treatments might include:- Lifestyle changes: Reducing or avoiding caffeine, alcohol, and tobacco; managing stress; and monitoring electrolyte balance.
- Medication: Beta-blockers or other antiarrhythmic drugs may be prescribed if the premature beats are frequent and bothersome.
- Electrophysiology study (EPS): In rare cases, this test is performed to identify serious irregular heart rhythms.
- Catheter ablation: A procedure used as a last resort for severe cases where other treatments have not been effective.
Prevention:
To minimize premature heartbeats, consider the following preventive measures:- Avoid triggers: Such as caffeine, alcohol, and tobacco.
- Manage stress: Through relaxation techniques, exercise, and adequate rest.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep.
