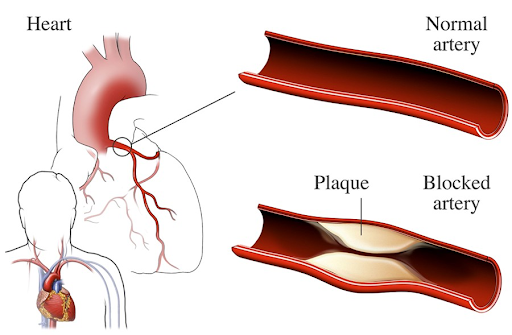
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also known as coronary heart disease, is a condition in which the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle, become narrowed or blocked. This blockage reduces the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle, increasing the risk of a heart attack and other cardiac complications.
Causes and Risk Factors
The primary cause of CAD is atherosclerosis, a process in which plaque (a mixture of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances) builds up inside the coronary arteries. This buildup can occur over many years and is often influenced by:- High levels of bad cholesterol (LDL) and low levels of good cholesterol (HDL)
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Unhealthy diet
- Age (risk increases with age)
- Family history of heart disease
- Chronic stress
Symptoms
The symptoms of coronary artery disease can vary, but they often include:- Chest pain or discomfort, often referred to as angina
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue with activity
- Heart attack
Diagnosis
Diagnosing CAD typically involves a review of medical history, physical examination, and various tests such as:- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
- Stress testing
- Echocardiogram
- Cardiac CT or MRI
- Coronary angiography
Treatment
Treatment for coronary artery disease aims to manage symptoms and reduce the risk of heart attacks. Treatment options include:- Lifestyle changes: diet, exercise, quitting smoking, and managing stress
- Medications: to lower cholesterol, control blood pressure, and prevent blood clots
- Procedures and surgeries: angioplasty and stent placement, coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)
