Obesity is a complex, chronic disease characterized by an excessive accumulation of body fat. It is associated with a range of health problems and an increased risk of various diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, hypertension, and certain cancers. Here’s a detailed overview based on current guidelines and recommendations:
Definition and Classification
1. Body Mass Index (BMI):
- White, Hispanic, and Black Individuals:
- Overweight: BMI of 25 to 29.9 kg/m²
- Obesity: BMI of ≥30 kg/m²
- Asian Individuals:
- Overweight: BMI of 23 to 24.9 kg/m²
- Obesity: BMI of >25 kg/m²
2. Waist Circumference:
- Provides additional information on abdominal obesity, which is a risk factor for cardiometabolic diseases.
- Elevated Waist Circumference:
- Males: ≥40 inches (102 cm)
- Females: ≥35 inches (88 cm)
- Asian Individuals:
- Males: ≥35 inches (90 cm)
- Females: ≥31 inches (80 cm)
- Elevated Waist Circumference:
Health Risks Associated with Obesity
Obesity is linked to numerous health conditions, including:
1. Cardiovascular Diseases:
- Heart disease
- Hypertension
- Stroke
2. Metabolic Disorders:
- Type 2 diabetes
- Metabolic syndrome
3. Respiratory Problems:
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Asthma
4. Gastrointestinal Issues:
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
5. Musculoskeletal Disorders:
- Osteoarthritis
- Joint pain
6. Reproductive and Urinary Conditions:
- Infertility
- Urinary incontinence
7. Psychological Issues:
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Low self-esteem
Management and Treatment
1. Lifestyle Modifications:
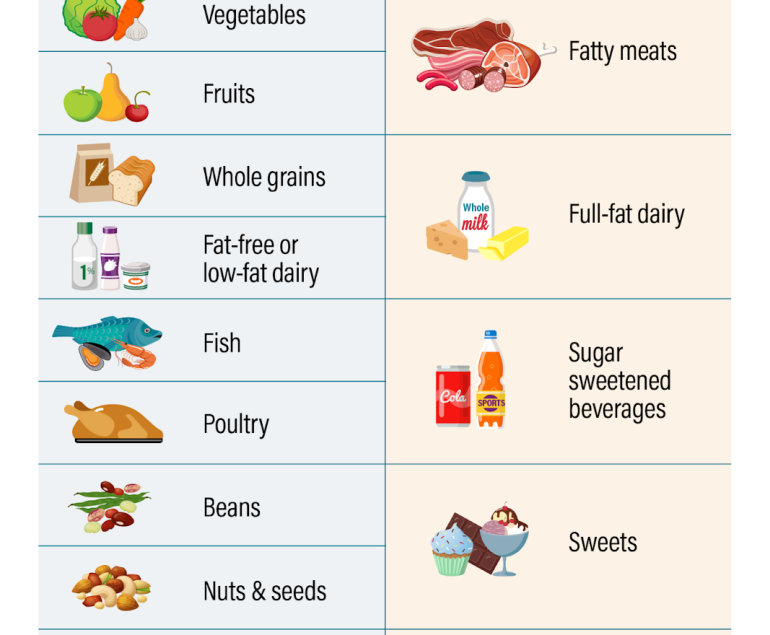
- Diet: Emphasis on a balanced, calorie-controlled diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise, including both aerobic and resistance training, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity activity per week.
- Behavioral Changes: Counseling and behavioral strategies to support sustainable lifestyle changes.
2. Medical Interventions:
- Pharmacotherapy: Medications to support weight loss in conjunction with lifestyle changes.
- Surgical Options: Bariatric surgery for individuals with severe obesity or those who have not responded to other treatments.
3. Monitoring and Support:
- Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers to monitor progress and adjust treatment plans as needed.
- Support groups and counseling to address psychological aspects and maintain motivation.
Prevention
1. Public Health Strategies:
- Promoting healthy eating and physical activity through community programs.
- Implementing policies to reduce the availability of unhealthy food options and increase access to nutritious foods.
2. Early Education:
- Teaching children and adolescents about healthy lifestyle choices to prevent the development of obesity from a young age.
Link:
https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/educational/lose_wt/BMI/bmi-m.htm